pCMV6-AC-mKate Mammalian Expression Vector
CAT#: PS100039
pCMV6-AC-mKate, mammalian vector with C-terminal mKate tag, 10ug
CNY 6080.00
货期*
现货
规格
| Cited in 4 publications. |
推荐一起购买 (3)
Specifications
| Product Data | |
| C-Tag | mKate |
| E. coli Selection | Ampicillin (100 ug/mL) |
| Cell Selection | Neomycin |
| Features |
|
| Download Vector Sequence | |
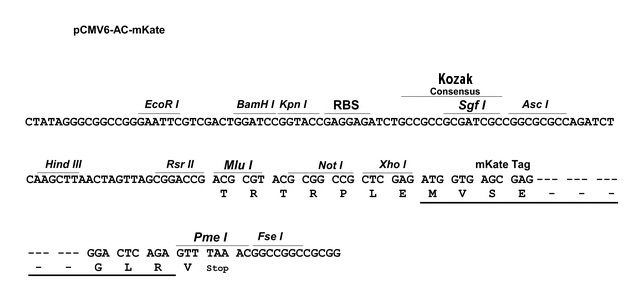
| Schematic of the multiple cloning sites |
|
Citations (4)
| The use of this Vectors has been cited in the following citations: |
|---|
|
Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition improves contractile function and restores transverse tubule loss and catecholamine responsiveness in heart failure
,Lawless, M;Caldwell, JL;Radcliffe, EJ;Smith, CER;Madders, GWP;Hutchings, DC;Woods, LS;Church, SJ;Unwin, RD;Kirkwood, GJ;Becker, LK;Pearman, CM;Taylor, RF;Eisner, DA;Dibb, KM;Trafford, AW;,
Sci Rep
,PubMed ID 31043634
[pCMV6-AC-mKate]
|
|
A missense mutation in SLC26A3 is associated with human male subfertility and impaired activation of CFTR
,null,
Scientific Reports
,PubMed ID 29079751
|
|
Governing effect of regulatory proteins for Cl(-)/HCO3(-) exchanger 2 activity
,Jeong, YS;Hong, JH;,
Channels (Austin)
,PubMed ID 26716707
[PS100039]
|
|
Essential role of carbonic anhydrase XII in secretory gland fluid and HCO3 − secretion revealed by disease causing human mutation
,null,
The Journal of Physiology
,PubMed ID 26486891
|
Documents
Resources
Customer
Reviews
Loading...




